Free online string to netstring creator. Just load your string and it will automatically get converted to a netstring. Load a string – get a netstring. There are no intrusive ads, popups or nonsense, just an awesome netstring encoder. Created for developers by developers from team Browserling.
Free online string to netstring creator. Just load your string and it will automatically get converted to a netstring. Load a string – get a netstring. There are no intrusive ads, popups or nonsense, just an awesome netstring encoder. Created for developers by developers from team Browserling.
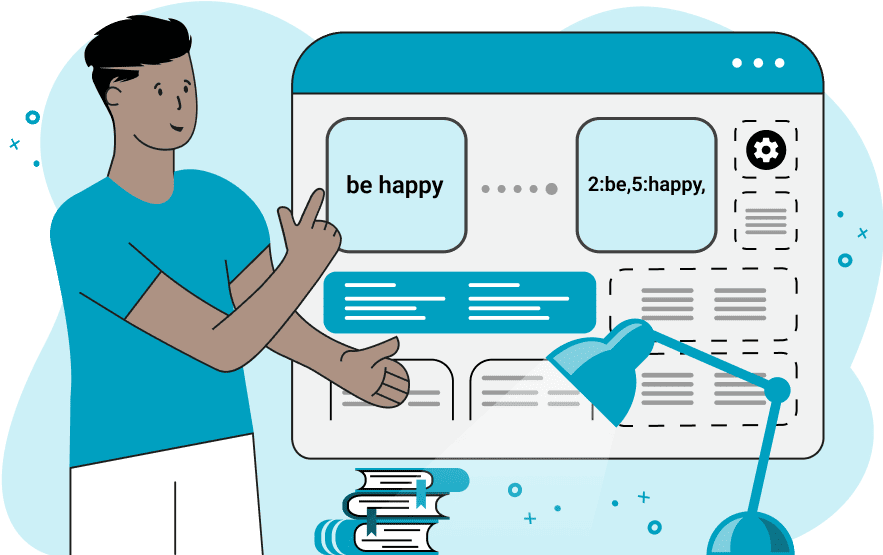
This browser-based tool constructs a netstring from a regular string. A netstring is a safe and reliable encoding method for transmitting regular strings as byte streams over networks or for serialization. It counts the number of 8-bit units in the string and stores this number in front of the string for easy parsing. A netstring can be represented in two different formats – as a length-prefixed string or as a series of hexadecimal numbers. A length-prefixed string format begins with ASCII digits that indicate the length of the data (number of bytes), then a colon, then the string itself, and a comma at the end. For example, the word "butterfly" gets encoded to "9:butterfly," and an empty string gets encoded to "0:,". In the hex format, the input string is first converted to UTF8 bytes and then these bytes are printed as hexadecimal values with a pair of angle brackets around them. In this case, the word "butterfly" gets encoded to <39 3a 62 75 74 74 65 72 66 6c 79 2c> and the empty line gets encoded to <30 3a 2c>. If your string contains several words, then it can be encoded in two ways – word-by-word or as a single long string. If you enter several text lines in the input, you can encode them as a whole or separately line-by-line. These encoding methods are easy to control via the "Encode Words" and "Multi-line" options. You can also activate the "Double Protection" option, which runs the netstring algorithm on the result the second time. If your string contains duplicate spaces, you can get rid of them via the "Skip Repeated Spaces" option. Also, you can prettify whitespace characters by replacing newlines with the "↵" symbol, regular spaces with the "⎵" symbol, and tabs with the "⇥" symbol. Stringabulous!
This browser-based tool constructs a netstring from a regular string. A netstring is a safe and reliable encoding method for transmitting regular strings as byte streams over networks or for serialization. It counts the number of 8-bit units in the string and stores this number in front of the string for easy parsing. A netstring can be represented in two different formats – as a length-prefixed string or as a series of hexadecimal numbers. A length-prefixed string format begins with ASCII digits that indicate the length of the data (number of bytes), then a colon, then the string itself, and a comma at the end. For example, the word "butterfly" gets encoded to "9:butterfly," and an empty string gets encoded to "0:,". In the hex format, the input string is first converted to UTF8 bytes and then these bytes are printed as hexadecimal values with a pair of angle brackets around them. In this case, the word "butterfly" gets encoded to <39 3a 62 75 74 74 65 72 66 6c 79 2c> and the empty line gets encoded to <30 3a 2c>. If your string contains several words, then it can be encoded in two ways – word-by-word or as a single long string. If you enter several text lines in the input, you can encode them as a whole or separately line-by-line. These encoding methods are easy to control via the "Encode Words" and "Multi-line" options. You can also activate the "Double Protection" option, which runs the netstring algorithm on the result the second time. If your string contains duplicate spaces, you can get rid of them via the "Skip Repeated Spaces" option. Also, you can prettify whitespace characters by replacing newlines with the "↵" symbol, regular spaces with the "⎵" symbol, and tabs with the "⇥" symbol. Stringabulous!
In this example, we convert three simple words to a netstring. We encode each word individually and print them together. As you can see, each word is encoded as its letter count, followed by a colon character, the word itself, and a comma. The spaces between the words aren't encoded because it's easy to deduce where they go (in place of commas).
This example applies the double protection algorithm to the quote by Oscar Wilde. First, it creates netstrings of all words and then recursively creates another netstring from the previous netstring.
In this example, we encode a list of music genres and output them in the hexadecimal netstring notation. This notation is the hexadecimal representation of a regular netstring wrapped in angle brackets. First, each genre is converted to a netstring, then all characters of this netstring are converted to base-16, and are placed between angle brackets. As the multi-line mode is active, we get eight separate hex netstrings for each genre.
In this example, we have loaded a quote by Bill Wilson as the input. Unfortunately, it contains many extra spaces that we don't really want to process. To remove them, we have activated the skip-duplicate spaces option. We also process each line and each word individually. As there are four lines and four words per line, we get sixteen netstrings in the output.
This example constructs a recursive netstring of a list of flowers. First, it counts the number of chars in every flower name and constructs a netstring for every flower. Then, it finds the length of this netstring and constructs a second netstring from it. The output format is selected as a hex-byte-string that prints the netstring chars as hex sequences between angle brackets.
In this example, we create one long netstring from nine shorter strings. The input contains different whitespaces and to make it more readable, we replace spaces with "⎵", tabs with "⇥", and newlines with "↵". Note that the regular space char has a length of 1 and contains one byte "0x20" but the UTF-8 symbol "⎵" is represented as three bytes "0xe2 0x8e 0xb5", so it has a length of 3. Similarly, tabs "⇥" have the length of 3 and so do newlines as "↵" has the length of 3.
You can pass input to this tool via ?input query argument and it will automatically compute output. Here's how to type it in your browser's address bar. Click to try!
Quickly edit a string in a browser-based editor.
Replace a set of strings with a new set of strings.
Convert a string to a title.
Convert a string to proper case.
Convert the first letter of every word in a string to uppercase.
Stretch out a string and align it along the left and right margins.
Align a string to the left.
Format and align a multi-line string.
Find how many letters there are in a string.
Find how many words there are in a string.
Find how many lines there are in a multi-line string.
Find how many paragraphs there are in a multi-line string.
Sort all letters in a string alphabetically.
Sort all words in a string alphabetically.
Sort a string that contains only numbers.
Reverse the order of all words in a string.
Reverse the order of all sentences in a string.
Find most frequent letters, words and phrases in a string.
Create a string with specific properties.
Generate a mnemonic for words in a string.
Rearrange letters in a string and create a new string.
Add line numbers to a multi-line string.
Wrap strings to the given line length.
Split a string into chunks of certain length.
Find syllables in a string.
Shuffle the order of all words in a string.
Find and extract all email addresses from a string.
Find and extract all web addresses from a string.
Make a string go in zigzags.
Make a string go in a circle.
Make a string go in a square or a rectangle.
Make a string go in a spiral.
Fit a string in an N-by-M block.
Find and extract all numbers from a string.
Analyze a string's complexity, including entropy.
Quickly convert a string to ROT18.
Encode a string to punycode.
Decode a string from punycode.
Convert a string to quoted-printable encoding.
Convert quoted-printable encoded data to a string.
Encode a string to base32.
Decode a string from base32.
Encode a string to base45.
Decode a string from base45.
Encode a string to base58.
Decode a string from base58.
Encode a string to Ascii85.
Decode a string from Ascii85.
Encode a string to UTF8.
Decode a string from UTF8.
Encode a string to UTF16.
Decode a string from UTF16.
Encode a string to UTF32.
Decode a string from UTF32.
Encode a string to IDN.
Decode a string from IDN encoding.
Convert a string to Unix-to-Unix encoding.
Convert Unix-to-Unix data to a string.
Convert a string to Xxencoding.
Convert an Xxencoded string to a regular string.
Strip all HTML tags from a string.
Remove all diacritical signs from a string.
Randomly add accent characters to letters in a string.
Remove punctuation marks and other symbols from a string.
Remove characters from a string.
Remove vowels from a string.
Remove consonants from a string.
Duplicate spaces in a string so one space becomes two.
Normalize string spacing and remove all duplicate spaces.
Visualy compare and find differences between two strings.
Calculate Levenshtein distance between two strings.
Calculate Hamming distance between two strings.
Find the longest common subsequence of two strings.
A tiny string rewriting system.
Limit the alphabet letters that are used in a string.
Convert a string to Unicode mess.
Remove Unicode mess from a string.
Create a list of all possible string typos.
Generate a mirror copy of a string.
Generate all 3-grams of a string.
Generate all ngrams of a string.
Generate n-skip-m-grams of a string.
Create a list of tokens from a string.
Lemmatize all words in a string.
Do stemming of all words in a string.
Extract fragments that match a regular expression in a string.
Split a string into fragments and extract the beginning parts.
Split a string into fragments and extract the ending parts.
Create a hyperstring from a string.
Create a regular string from a hyperstring.
Create an array of characters from a string.
Split a string into characters and return their integer values.
Put digits in place of characters in a string.
Correct misquoted strings (add/remove missing quotes).
Shift characters in a string to the left or right.
Create a colorful string.
Create a SEO-friendly URL from a string.
Substitute random characters in a string and make errors.
Run a spell checker and find mistakes in a string.
Interleave two strings character by character.
Duplicate characters in a string multiple times.
Draw a string on an LCD screen.
Create a string that doesn't have too many characters.
Create a string that has many characters.
Generate a string with a certain amount of characters.
Create two strings that have the twin property.
Create three strings that have the triplet property.
Generate a word cloud from all words in a string.
Split a string into multiple substrings.
Subscribe to our updates. We'll let you know when we release new tools, features, and organize online workshops.
Enter your email here
We're Browserling — a friendly and fun cross-browser testing company powered by alien technology. At Browserling we love to make peoples' lives easier, so we created this collection of online string tools. All our tools share the same user interface so as soon as you learn how to use one of the tools, you'll instantly know how to use all of them. Our online string tools are actually powered by our web developer tools that we created over the last couple of years. Check them out!